Publisher: Supplier of LED Display Time: 2022-11-28 14:05 Views: 1479
In order to achieve the best display effect, a high-quality LED display generally needs to be calibrated for brightness and color, so that the brightness consistency and color consistency of the LED display can be the best after lighting, so why is the high-quality LED display Correction required, and how? Next, Liancheng sent the editor to let everyone take a look!
PART.1
First of all, it is necessary to understand the basic characteristics of the brightness perceived by the human eye. The actual brightness perceived by the human eye and the actual brightness emitted by an LED display are not linear, but a nonlinear relationship.
For example, when the human eye sees an LED display with an actual brightness of 1000 nit, we reduce the brightness to 500 nit, and the actual brightness is reduced by 50%, but the perceived brightness of the human eye does not decrease linearly to 50%, but only to 73%.
The nonlinear curve between the perceived brightness of the human eye and the actual brightness of the LED display is called the gamma curve (as shown in Figure 1). It can be seen from the gamma curve that the human eye's perception of brightness changes is relatively subjective, which is not consistent with the actual brightness change range of the LED display.
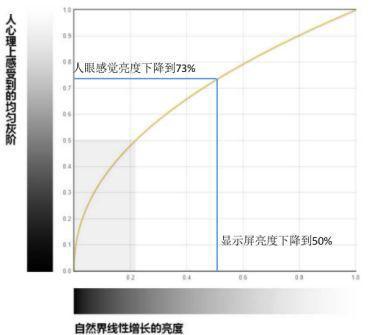
Figure 1 Gamma curve
PART.2
Next, let's understand the characteristics of the human eye's perception of color changes. Figure 2 is the CIE chromaticity diagram. Colors can be represented by color coordinates or light wavelengths. For example, the wavelength of a common LED display is 620 nanometers for red LEDs, 525 nanometers for green LEDs, and 470 nanometers for blue LEDs.
Generally speaking, in a uniform color space, the human eye's tolerance for color difference is △Euv=3, also known as visually perceptible color difference. When the color difference between LEDs is less than this value, it is considered that the difference is not large. When △Euv>6 means that the human eye perceives serious color difference between the two colors.
Or it is generally believed that when the wavelength difference is greater than 2-3 nanometers, the human eye can perceive chromatic aberration, but there are still differences in the sensitivity of the human eye to different colors, and the wavelength difference that the human eye can perceive for different colors is not fixed.
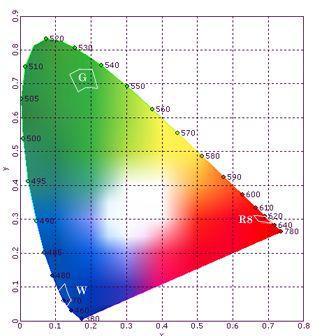
Figure 2 Chromaticity coordinate diagram
Judging from the changes in brightness and color of the human eye, the LED display needs to control the brightness and color differences within the range of differences that the human eye cannot perceive, so that the human eye will feel that the brightness and color are consistent when viewing the LED display. sex is better. The brightness and color range of LED packaging devices or LED chips used in LED displays have a great impact on the consistency of display.
For example, an LED packaging device from Ledman uses light and color separation, and the brightness range of red light is 1840mcd-2400mcd, and the brightness span is 30%. The output rate of green light wavelength 520nm-523nm is 92%, and the output rate of 517nm-520nm is 8%.
PART.3
When making LED displays, you can choose LED packaging devices with brightness and wavelength within a certain range. For example, you can choose LED devices with a brightness span of 10%-20% and a wavelength range of 3 nanometers. In Figure 3, the LED red light brightness can be selected from 1980-2180mcd main-range devices, and the LED green light wavelength can be selected from 520-523 nm main-range devices.
Selecting LED devices with narrow brightness range and narrow wavelength range can basically ensure the display consistency of the display screen to achieve better results.
However, the brightness range and wavelength range of the LED packaging device actually selected by the general LED display screen may be larger than the ideal range above, which leads to the difference in brightness and color of the LED light-emitting chip that may be seen by the human eye.
Another situation is COB packaging. Although the brightness and wavelength of LED light-emitting chips can be controlled within the ideal range, it will also lead to inconsistencies in brightness and color.
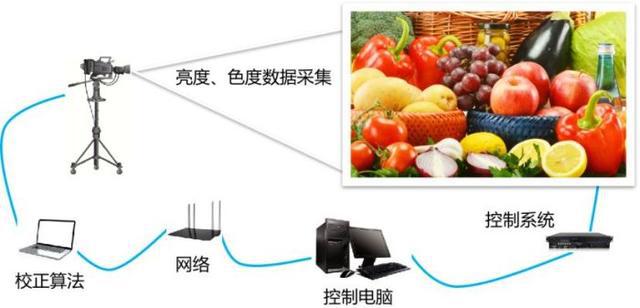
Figure 5 Point-by-point correction of LED display
In order to solve this inconsistency of the LED display and improve the display quality, point-by-point correction technology can be used.
point-by-point correction
Point-by-point correction is to collect the brightness and chromaticity data of each sub-pixel on the LED display, give the correction coefficient of each primary color sub-pixel, and feed it back to the control system of the display screen, and the control system applies the correction coefficient , to achieve differential driving of each primary color sub-pixel, thereby improving the brightness, chromaticity uniformity and color fidelity of the display screen.
summary
The human eye's perception of the brightness change of the LED light-emitting chip has a nonlinear relationship with the actual brightness change of the LED light-emitting chip. This curve is called the gamma curve. The sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths of colors is different, and the LED display screen shows The effect is better, and the brightness and color differences of the display screen should be controlled within the range that cannot be recognized by the human eye, so that the LED display screen can show better consistency.
The brightness and wavelength of LED packaged devices or COB packaged LED light-emitting chips have a certain range. In order to make the LED display screen show better consistency, point-by-point correction technology can be used to achieve high-quality LED display brightness and chromaticity. Consistent, improve the display quality of the display.
Source: Projection Times